The Reynolds number is used to determine if a flow is laminar or turbulent. It can be calculated with the following equation, the details of which can be found here.
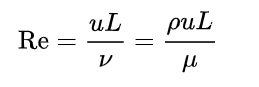
The data you will need are the material properties of the fluid (rho and mu), the velocity (u) and a length scale (L).
For internal flow in a circular pipe, the velocity refers to the average velocity within the pipe, and the length scale corresponds to the pipe's diameter. In the case of symmetric or axisymmetric simulations, the actual diameter of the pipe will be twice the value used in the meshed geometry. If the Reynolds number, calculated using these parameters, exceeds approximately 3,000, the flow is most likely turbulent.